query processing
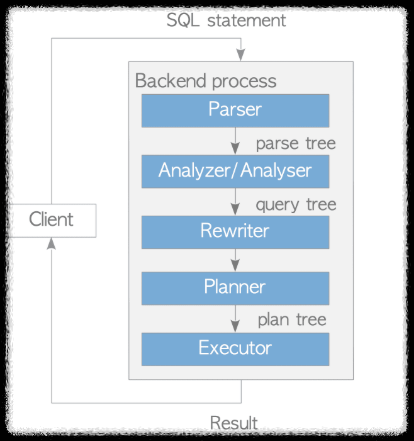
parser
SQL 문을 읽을 수 있도록 parse tree를 생성함.
parse tree를 만들 때 SQL 문법 오류(syntax check)를 확인
sementic check는 analyzer에서 진행함.
즉, syntax 오류가 없으면 DB 내 table이 없더라도 parser 단계는 통과할 수 있음.
parse tree 예시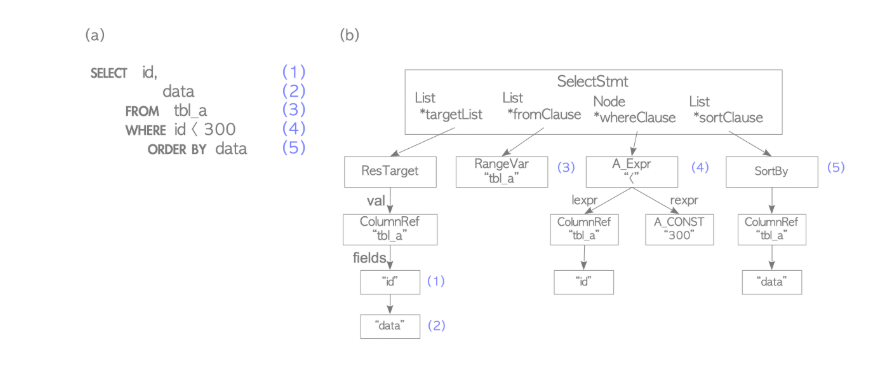 |
analyzer
parser 단계에서 생성된 parse tree의 semantic analysis를 진행 후 query tree를 만듬.
| targetlist: select 절의 columns 목록 range table: query에서 사용된 relations list를 저장 join tree : from 절과 where절을 저장 sortClause: sort나 group 절을 저장  |
rewriter
system catalog인 pg_rules에 저장된 규칙에 따라 query tree를 변환하는 작업을 함.
아래 예시는 view를 table로 변환하는 과정을 보여줌.
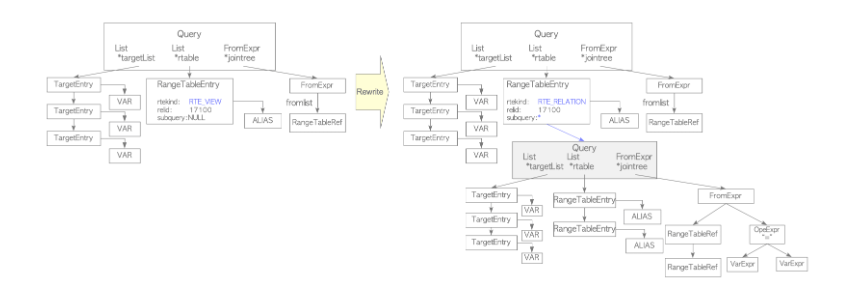 |
planner와 executor
rewriter로부터 query tree를 받고 executor가 효과적으로 처리할 수 있는 plan tree를 생성
cost-based optimization으로 plan을 세움. (rule-based는 지원하지 않음.)
PostgreSQL은 hint를 제공하지 않으나 pg_hint_plan extension을 사용하면 쓸 수 있음.
| plan tree는 plan nodes로 구성됨. 아래 그림에서 query plan에서 cost 정보가 있는 각각의 line을 plan node라고 보면됨. 각 plan node에는 executor가 처리하는 데 필요한 정보를 가지고 있음. single table query의 경우, executor는 가장 마지막 라인에서 첫번 째 라인 순으로 query를 처리함. 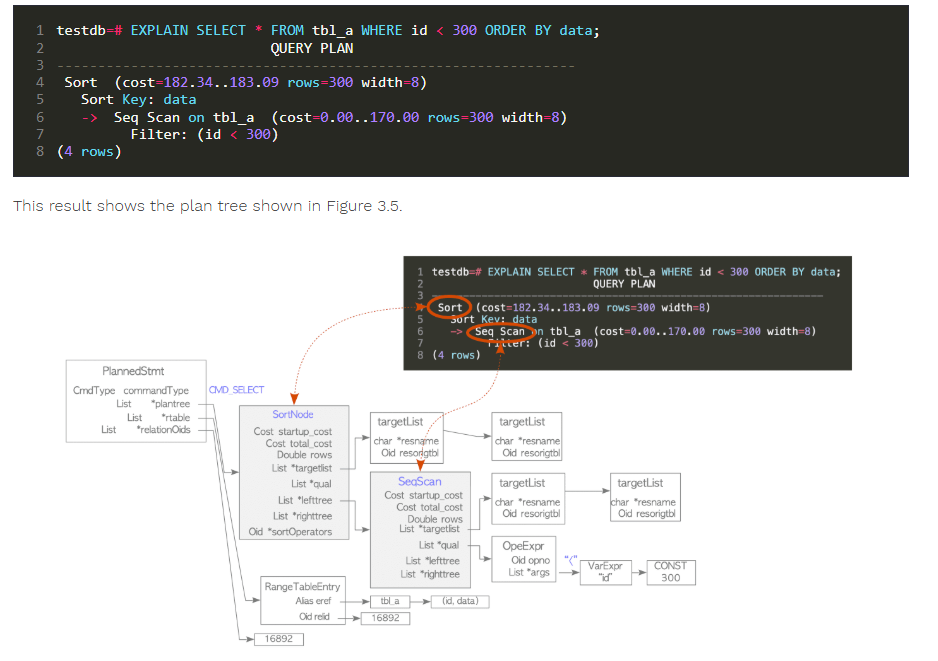 |
'PostgreSQL' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 24. PostgreSQL - Temporary Files (4) | 2024.12.30 |
|---|---|
| 23. PostgreSQL - planner의 cost 계산 (1) | 2024.12.29 |
| 21.PostgreSQL - WAL(Write Ahead Log) (4) | 2024.12.28 |
| 20. PostgreSQL - buffer manager (4) | 2024.12.25 |
| 19. PostgreSQL - index-only scans (3) | 2024.12.25 |


