Heap-Only Tuple이란?
PostgreSQL 8.3부터 도입됨.
updated row가 old row가 저장된 table page에 저장될 때 index와 table의 page를 효율적으로 사용하는 방법을 의미.
HOT 도입 이유
1. index와 table page의 공간 낭비를 줄인다.
- update된 row의 column이 index column이 아니라면 HOT 이용 시 pruing 작업으로 인해 table 내 tuple이 생성될 때마다 index tuple을 insert하지 않아도 됨.
- defregment 작업으로 vacuum이 수행되지 않더라도 table내 dead tuple을 정리할 수 있음.
2. resource 낭비를 줄인다.
- HOT의 defragment로 vacuum대신에 dead tuple을 정리해주므로 vacuum이 처리해야할 dead tuple 수를 줄일 수 있음.
Heap-Only Tuples 사용을 위한 조건
1. table update 시 normal index, expression index, partial indexes의 index column은 수정되지 않아야 함.
2. update된 row에 대한 old version row를 포함하는 page에는 충분한 여유 공간이 있어야 함.
HOT 도입 전 row update 동작 과정
아래 그림을 보며 설정
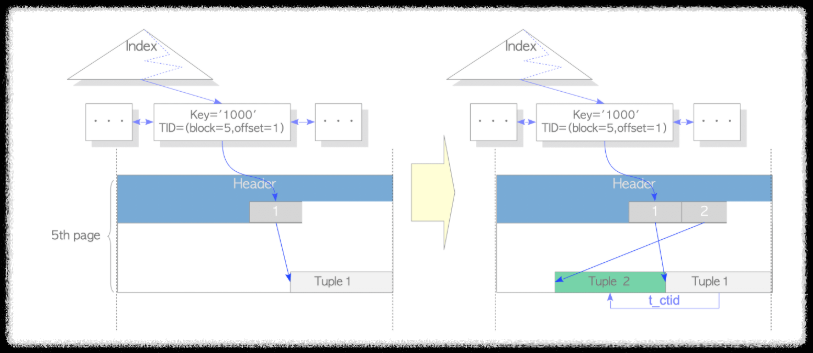
(a) 1000개의 tuple을 가진 table이 있고 마지막 tuple인 1000은 5번째 page의 첫 번째 tuple로 저장되어 있음.
(b) HOT를 사용하지 않고 update했을 때 동작 과정
index page에 index tuple이 추가되고 table tuple도 insert됨.
즉, 추가된 table tuple을 가리키는 index tuple을 만들어야 해서 index page 내에 같은 key로 생성된 index tuple이 중복되어 여러개 생성될 수 있고 이로 인해 공간 낭비가 발생하게 됨.
또한, index tuple을 insert하고 vacuum하는 것은 비용이 많은 듬.

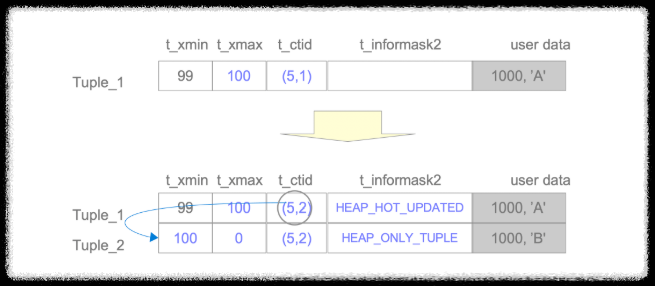
Heap-Only Tuple의 동작 과정
update된 row가 old row와 같은 table page에 저장될 경우 HOT 동작
index page내 index tuple이 추가되지 않음.
table page의 tuple 내 t_informask2 field에 아래 2개의 bit가 old row와 new row에 각각 기록됨.
HEAP_HOT_UPDATED - old row의 tuple header의 t_informask2에 기록
HEAP_ONLY TUPLE - new row의 tuple header의 t_informask2에 기록
2개의 bit 값은 HOT의 pruning과 defragment 동작과는 무관함.
HOT - pruning 작업 수행
| 들어가기 전에 수행한 query가 page의 tuple을 찾아가는 과정 정리 page내 tuple이 생성될 때 line pointer가 같이 생성되고 생성된 line pointer는 tuple을 가리키도록 되어 있음. index tuple의 경우엔 table을 가리키는 TID를 갖고 있으며 line pointer로 연결됨. 즉, index scan으로 값을 찾아간다고 했을 때 아래와 같이 동작함. index tuple => table page 내 line poointer => table page내 tuple로 연결되는 구조 |
pruning
HOT 수행 후 select, insert, update, delete와 같은 명령이 수행될 때 가능하다면 pruning 작업을 진행하게 됨.
정확히 언제 pruning이 발생하는지 자세히 알고 싶다면 클릭.
| pruning 작업의 의미 index page의 tuple과 연결된 table page의 line pointer를 dead tuple이 아니라 live tuple을 가리키는 line pointer로 변경하는 작업을 믜미 |
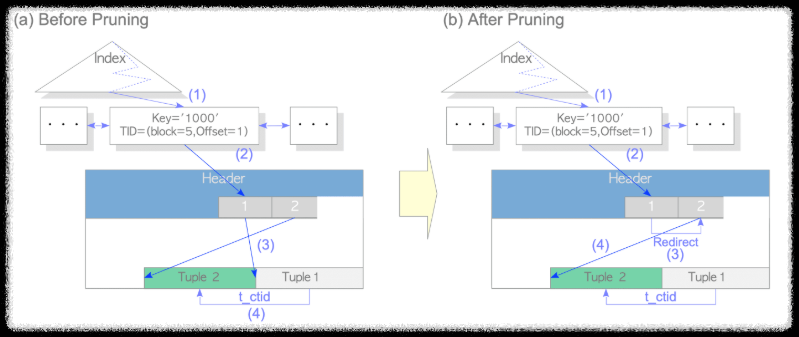
위의 그림으로 pruning이 진행되기 전과 후를 비교
(a) pruning 전
table tuple을 가리키는 index tuple을 찾음.
index tuple에 저장된 정보로 table page내 line pointer에 접근
dead tuple로 접근
dead tuple 내 t_ctid를 확인 후 live tuple로 접근
pruning 작업을 하지 않으면 table page에서 dead tuple이 제거될 때 문제가 발생함.
즉, index tuple이 가리키는 dead tuple이 사라지게 되면 live tuple을 찾아갈 수 없는 이슈가 생김.
그래서 pruning 작업으로 index tuple이 가리키는 line pointer를 live tuple을 가리키는 line pointer로 redirect되도록 함.
(b) pruning 후
table tuple을 가리키는 index tuple을 찾음.
index tuple에 저장된 정보로 table page내 line pointer에 접근
live tuple을 가리키는 line pointer로 redirect 됨.
redirect된 line pointer에서 live tuple 값을 찾음.
HOT - pruning 작업 수행 시 defragment도 진행
| defragment란? pruning 작업 시 dead tuple을 가리키는 line pointer를 live tuple을 가리키는 line pointer로 변경한다고 했는데 이 때 dead tuple을 같이 정리해 버림. 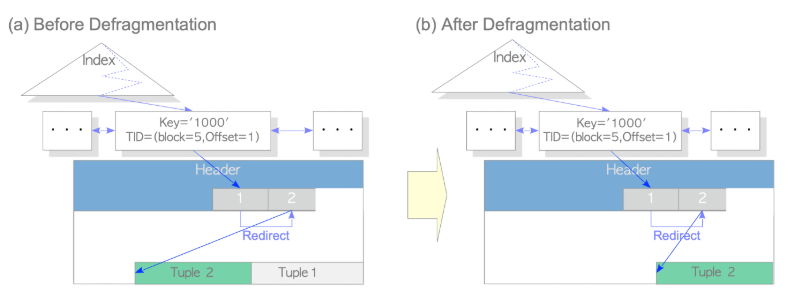 defragment의 장점 index tuple을 정리하지 않기 때문에 vacuum보다 리소스 비용이 덜 필요함. |
HOT를 이용할 수 없는 case
아래 2가지 case 모두 index tuple이 추가되는 것을 알 수 있다.
(a) old row가 있는 page가 아니라 다른 page에 update된 row가 저장될 경우
(b) index column 값이 update될 경우

Heap-Only Tuple을 이용하기 위한 튜닝 포인트
- HOT updates를 위해 page 공간을 충분히 확보하기 위해 table의 fillfactor의 크기를 줄일 수 있음.
- 기존 page에 new row version을 위한 충분한 공간이 없으면 새 page로 migration되어야 하는데 이 때는 HOT updates를 할 수 없음.
- pg_stat_all_tables view로 HOT와 non-HOT updates의 발생을 모니터링 할 수 있음.
select relid, schemaname, relname, n_tup_hot_upd, n_tup_newpage_upd from pg_stat_all_tables where schemaname = 'test' and relname = 'test_tab'; relid | schemaname | relname | n_tup_hot_upd | n_tup_newpage_upd -------+------------+----------+---------------+------------------- 24827 | test | test_tab | 0 | 0
참고
'PostgreSQL' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 20. PostgreSQL - buffer manager (4) | 2024.12.25 |
|---|---|
| 19. PostgreSQL - index-only scans (3) | 2024.12.25 |
| 17. PostgreSQL - vacuum full (3) | 2024.12.25 |
| 16.PostgreSQL - autovacuum (4) | 2024.12.25 |
| 15. PostgreSQL - VACUUM (3) | 2024.12.22 |


